#Slow-Release Plant Nutrients Industry
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Latest Regulatory Trends Impacting the Controlled-release Fertilizers Market
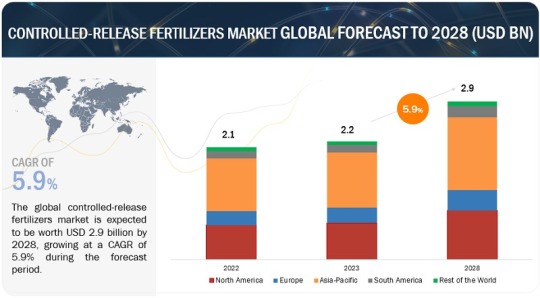
The global controlled-release fertilizers market is projected to reach USD 2.9 billion by 2028 from USD 2.2 billion by 2023, at a CAGR of 5.9% during the forecast period in terms of value. The controlled-release fertilizers market has witnessed significant growth and established its dominance in the global agriculture industry. According to the World Bank Report 2023, approximately 9.2% of the world’s population faced hunger in 2022, compared with 7.9% in 2019. The rising levels of hunger and food insecurity highlight the urgent need to increase agricultural productivity to ensure food availability. Thus, the increasing demand for enhanced agricultural output while reducing environmental effects is one of the main driving factors. These fertilizers deliver nutrients gradually, enhancing plant absorption while lowering leaching and runoff, which helps reduce water pollution. Furthermore, the use of controlled-release fertilizers is accelerated by the push for sustainable agricultural practices, which are complementary to their advantages.
Download PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=136099624
YARA
Yara is primarily engaged in manufacturing and marketing fertilizers and industrial products. The company operates through major business segments, namely, fertilizer and chemical products, freight, and insurance services. Yara is a leading player in global crop nutrition and operates a global leading ammonia and nitrates capacity. Deep agronomic knowledge, crop nutrition solution, and digital capabilities enable Yara to work toward climate positive future. The company offers a wide range of controlled-release fertilizers including YaraBela, YaraVita, YaraVera, and YaraMila. These fertilizers typically consist of granules that contain a blend of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with other secondary and micronutrients. The nutrients are encapsulated within a polymer coating or other controlled-release matrix, which determines the rate at which the nutrients are released into the soil. In September 2021, Yara acquired Ecolan (US), a producer of fertilizers for agriculture and forestry, to expand its organic fertilizer business. This was Yara’s first acquisition in the organic fertilizer segment. This would help improve nutrient use efficiency in this segment by capitalizing on deep crop nutrition knowledge. Yara's goal of enhancing nutrient use efficiency across different farming systems resonates with the benefits of controlled-release fertilizers.
Nutrien Ltd.
Nutrien Ltd. is one of the leading producers of crop inputs, services, and solutions. The company operates its business in Nitrogen, Potash, Phosphate, and Retail segments. The company focuses to produce and distribute more than 27 million tonnes of potash, nitrogen, and phosphate products for agricultural, industrial, and feed customers throughout the world. The company has the most extensive crop nutrient product portfolio, combined with its global retail distribution network, which includes more than 1,500 farm retail centers. In the premium technologies segment, the company offers “ESN Smart Nitrogen” which is a controlled-release fertilizer that minimizes nitrogen loss and maximizes crop yield. ESN technology uses a flexible polymer coating to encapsulate a urea granule comprised of 44% nitrogen. The unique coating protects and releases nitrogen based on soil temperature. ESN provides nitrogen based on the demand for the growing crop.
In July 2022, Nutrien Ltd. entered into an agreement to acquire Brazilian company Casa do Adubo S.A. (Casa do Adubo). The acquisition includes 39 retail locations, under the brand Casa do Adubo, and 10 distribution centers, under the brand Agrodistribuidor Casal, in the states of Acre, Bahia, Espirito Santo, Maranhao, Mato Grosso, Minas Gerais, Para, Rio de Janeiro, Rondonia, Sao Paulo, and Tocantins. The acquisition expands the company’s footprint in Brazil from five states to 13 and supports growers in a key region of the world that increasingly rely on to sustainably increase crop production and feed a growing population. With a larger footprint and increased market presence, Nutrien could potentially expand its product offerings to include a wider range of agricultural inputs, including specialized fertilizers like controlled-release fertilizers.
Request Sample Pages: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/requestsampleNew.asp?id=136099624
Mosaic
The Mosaic Company is one of the leading producers, marketers, and distributors of concentrated phosphate and potash crop nutrients. The company is organized into Phosphates, Potash, and Mosaic Fertilizantes business segments. The company mines its phosphate products from its own land in Central Florida, US, and also through its joint venture in Peru. The company offers high-quality controlled-release fertilizers and distributes its products to countries in North America and worldwide. The company has three business segments—phosphates, potash, and Mosaic Fertilizantes.
By leveraging their expertise, Mosaic Controlled-release fertilizers are committed to providing innovative solutions that improve crop quality, enhance nutrient intake, and contribute to overall plant growth over the globe. In March 2021, Mosaic entered into a strategic partnership with AgBiome to pioneer new biological alternatives that enhance soil health and fertility. This collaboration illustrates a larger industry trend toward sustainable agriculture solutions, particularly in the field of controlled-release fertilizers. The Mosaic Company and AgBiome are targeting innovative goods that not only help growers maximize nutrient use efficiency but also reduce fertilizer loss to the environment.
Argentina is expected to be the fastest-growing market in the South American region during the forecast period.
Argentina is poised to emerge as the fastest-growing player in the controlled-release fertilizers market within South America. Argentina places considerable emphasis on sustainable farming practices, aligning with global trends and consumer preferences. Controlled-release fertilizers offer a solution to minimize nutrient runoff, reduce environmental impact, and promote soil health, making them a natural fit for the country's sustainable agriculture initiatives.
#Slow-Release Plant Nutrients Industry#Extended Nutrient Delivery Industry#Long-Lasting Fertilizer Benefits Industry#Controlled-Release Fertilizer Technology Industry#Timed Nutrient Dispersal Industry#Efficient Fertilizer Application Industry#Sustainable Nutrient Release Industry#Fertilizer for Crop Growth Industry#Crop Nutrient Management Industry#Precision Fertilization Industry
0 notes
Text
Agriculture is a big source of emissions. In the US, about 10 percent of greenhouse gases come from livestock or crops—and for a long time, agriculture has lagged behind other sectors when it comes to cutting its carbon footprint. Since 1990, total emissions from agriculture have risen by 7 percent, while emissions from sectors like electricity generation and buildings have declined.
There’s a simple reason for this: Cutting emissions from agriculture is really hard. It’s not like the energy industry, which has readily available low-carbon electricity in the form of renewables. Reducing agriculture’s impact means making tough decisions about what gets farmed and how, and dealing with the notoriously tricky science of making sure carbon stays in the ground rather than being released into the atmosphere.
The US has started getting to grips with these tough decisions. President Biden’s Inflation Reduction Act included $20 billion to help farmers tackle the climate crisis. And in February 2022 the US Department of Agriculture announced $3.1 billion in funding through a scheme called Partnerships for Climate-Smart Commodities (PCSC). The money was intended to fund projects that help farmers adopt more environmentally friendly ways of farming and create a market for what the USDA calls “climate-smart” crops and livestock.
According to the USDA, its plan has the potential to sequester 60 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalents—the same as removing 12 million gasoline-powered cars from roads for one year. But some scientists are worried that the PSCS approach is the wrong kind of climate intervention. The government could be channeling billions of dollars to projects that are of uncertain benefit in terms of emissions—or, worse, actually end up increasing overall levels of greenhouse gases.
If the goal is to reduce overall emissions from agriculture, a good place to start is by figuring out where all those emissions come from. It turns out that over half of all agricultural emissions come in the form of nitrous oxide—a potent greenhouse gas released when microbes in the soil break down nitrogen-based fertilizers. Overuse of fertilizer is a huge problem in agriculture, says Paul West, an ecologist at the climate nonprofit Project Drawdown. On top of being a huge source of emissions, excess nitrogen leaches into waterways, causing algal blooms.
Reducing the amount of fertilizer farmers use would be a big win. Remote sensors and machines can help farmers apply fertilizer only when and where it is needed, while smarter forms of fertilizers might reduce the amount of nitrogen that ends up digested by microbes. The crucial thing about these kinds of interventions is that they stop emissions being released in the first place, says Dan Blaustein-Rejto, director of food and agriculture at the Breakthrough Institute. If you never put fertilizer on the ground, it’s impossible for microbes to turn it into planet-warming nitrous oxide. Getting smarter with fertilizer use is one of the biggest changes that US agriculture could make to its emissions footprint.
But fertilizer management plays second fiddle to a different kind of climate project in the PCSC. Of the 60 finalized projects for which the USDA has published summaries, only 12 mention nutrient management or fertilizer application. A much higher number of projects focus on cover cropping—a technique that involves covering fields with crops between harvests in order to slow soil erosion, capture carbon, and keep nutrients in the fields. Since planting cover crops takes time and expense, and can lower the overall productivity of fields, only a relatively small number of farmers use the technique. If the PCSC is successful, however, the number of farmers planting cover crops should shoot up.
Cover crops absorb carbon from the atmosphere and turn it into plant material as they grow, explains Deepak Joshi, an assistant professor at Arkansas State University and the author of a recent paper about cover crops. When the cover crops are harvested or left to rot on the soil, a lot of that carbon gets released back into the atmosphere, but a small amount can remain behind in the soil. If that soil remains undisturbed, then that carbon can potentially remain underground for years. Joshi’s meta-analysis focused on cover crops grown in cornfields around the world and found that, on average, cover crops increased carbon stored in the soil by about 7 percent.
So far, so good. But once you dive down into the details of Joshi’s study, things get more complicated. The research found that the amount of carbon stored varied widely, depending on location, cover crop type, plowing, and the amount of plant growth. A different review, this time examining cover cropping on US farms, found that, in lots of cases, fields with cover crops didn’t gain extra soil carbon when compared to fields that hadn’t been cover cropped. “In terms of climate benefit, it isn’t all that great,” says West.
One of the big limitations to cover cropping is that carbon added to the soil might eventually make its way back into the atmosphere. “What we find is that even where there is a build-up of carbon, once you plow those areas again you lose a lot—or all—of the carbon that has been stored up over time,” says West. If money for cover crops runs out, farmers may start leaving fields bare during off-seasons and plowing them more, which would mean a lot of that sequestered carbon would end up back in the atmosphere. And if the cover crops reduce the overall productivity of fields, there’s also the danger that the practice might encourage more land to be converted to agriculture, which is bad news for overall emissions.
Blaustein-Rejto and West both worry that the PCSC prioritizes sequestering carbon rather than stopping emissions from being released in the first place. One way to think about this is the difference between switching to an electric car today or continuing to drive a gas-powered vehicle while also planting a forest to sequester the carbon you emit. In both cases the overall carbon accounting may net out the same, but sequestering always carries the risk that the carbon might later be released if—for instance—that forest is replaced by a cattle ranch.
Robert Bonnie, the under secretary for agriculture for farm production and conservation at the USDA, says that criticisms of the PCSC aren’t entirely fair. “These are pilots. We’re actually going to go out and try some things. We don’t have all the information we need,” he says. He points out that a number of the funded projects do focus on fertilizer use. “We’re not scared of the math; we’re really interested in getting the math right,” he says.
Bonnie says that the real challenge is to persuade farms to get on board with climate-smart farming. A big focus of the project is to create a market for climate-smart crops and livestock, encouraging buyers to pay a premium for goods made in an environmentally friendly manner. A top-down regulatory approach might discourage farmers from taking part, he says.
In lots of the PCSC projects, the USDA funding is supplemented by money from food companies that buy beef, corn, soy, or other agricultural commodities. One PCSC project run by the Iowa Soybean Association includes $62.1 million in corporate payments from companies including PepsiCo, Cargill, Target, JBS, and Coca-Cola. This is a relatively new form of carbon accounting called insetting, where companies pay for carbon offsets within their own supply chains.
Insetting is rising in popularity, but it has a lot of the same problems as offsets, says Sybrig Smit of the NewClimate Institute, a climate policy and global sustainability nonprofit based in Germany. It might be difficult to assess whether insets deliver their supposed benefits, and sequestering carbon is still less desirable than cutting emissions at their source, particularly when it helps sustain industries that are bigger emitters of carbon. Livestock is the second-biggest source of emissions in US agriculture, so reducing consumption of meat and dairy products is an obvious way to reduce emissions, says Smit. “As a society we’re really scared to touch on our consumption patterns,” she says.
The USDA scheme is stuck in an awkward place. It is supposed to reduce emissions but seeks to achieve that in a way that keeps farmers on board and doesn’t fundamentally change the goods they produce. “We’re going to have beef production and dairy production for a long time to come. And our job is to figure out how to work with those producers to reduce the greenhouse gas impacts to the maximum extent we can,” Bonnie says.
In practice, that means that much money from PCSC will go toward farming soy and corn—a large percentage of which will end up as livestock feed or as ethanol for biofuels. Cover cropping is good for soil health, but its potential to lead to long-lasting carbon storage is uncertain at best. At worst, it could see the US avoiding the kind of fundamental changes to food production that could really bring emissions down.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Casein Glycomacropeptide Market Growth Trends: Exploring Key Drivers, Challenges, and Opportunities for Future Expansion
The global casein glycomacropeptide market is seeing remarkable growth due to increasing demand for protein-based supplements, advancements in healthcare, and a rise in consumer awareness regarding nutritional benefits. Casein glycomacropeptide is a bioactive protein derivative found in cow’s milk, which has gained attention for its multifaceted health benefits, particularly in managing lactose intolerance and supporting immune function. As consumer focus shifts toward clean-label products, fortified with natural ingredients, CGMP is finding its way into a variety of applications, especially in functional foods, sports nutrition, and infant formula.

Market Dynamics: Drivers of Growth
One of the most significant trends fueling the market’s growth is the increasing number of people opting for alternative protein sources, such as casein glycomacropeptide. CGMP is often used in products catering to individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies, making it a valuable asset in the nutritional industry. As awareness of gut health and immunity has become more prevalent, CGMP’s prebiotic properties, which support the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, have positioned it as a go-to ingredient in functional foods.
Another major driver is the growing popularity of sports nutrition. CGMP, with its slow-release protein properties, aids in muscle repair and growth, making it an essential addition to protein supplements for athletes. Since it digests more slowly compared to other proteins, CGMP provides sustained amino acid release, which helps support muscle recovery and growth over an extended period.
Key Applications of Casein Glycomacropeptide
The casein glycomacropeptide market has penetrated several industry verticals including:
Sports Nutrition: The rising demand for health-conscious products is leading to a significant upturn in sports supplements that include CGMP as a key ingredient due to its muscle-recovery benefits.
Infant Formula: Due to its bioactive properties and its benefits to gut health and immunity, CGMP is extensively used in baby formulas for better digestion and nutrient absorption.
Functional Foods and Beverages: CGMP is increasingly used in functional foods, such as yogurt, protein bars, and ready-to-drink nutritional beverages, due to its digestive and immune system benefits.
Health Supplements: With a surge in preventative healthcare, many dietary supplement brands have incorporated CGMP in products targeted at improving immunity, digestive health, and overall well-being.
Region-Wise Market Growth
In terms of regional demand, North America and Europe continue to dominate the casein glycomacropeptide market, driven by heightened consumer awareness, the adoption of healthier lifestyles, and a growing base of sports nutrition customers. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, such as India and China, are expected to witness significant growth in the coming years. As these regions increasingly embrace health-conscious living, CGMP is poised to capture a larger market share as consumers demand enhanced nutritional options.
In addition, the trend of veganism and plant-based alternatives is providing a unique opportunity for CGMP, as it positions itself as a plant-based, dairy-derived, but allergen-friendly alternative to traditional milk proteins. This shift toward clean-label, free-from products that cater to consumers with dietary restrictions or preferences is driving CGMP's future potential in the broader market.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the promising growth, the market for casein glycomacropeptide does face several challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the supply constraints and high production costs associated with casein protein extraction. Furthermore, regulatory concerns and a lack of comprehensive understanding of CGMP’s long-term health benefits may restrain its broader market penetration in some regions. However, companies that focus on overcoming these challenges through research, effective supply chain solutions, and transparency about the benefits of CGMP will likely gain a competitive edge.
Looking ahead, the global casein glycomacropeptide market is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5-7% over the next few years. Innovations in production processes, such as enzymatic processing, coupled with the increasing demand for clean-label, functional foods, suggest that CGMP will continue to have a vital role in transforming the future of nutrition and health industries worldwide.
0 notes
Text
Agricultural Secondary Nutrients Market
Agricultural Secondary Nutrients Market Size, Share, Trends: Nutrien Ltd. Leads
Rising Adoption of Precision Agriculture and Customized Nutrient Management
Market Overview:
The Agricultural Secondary Nutrients Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2024 to 2031, reaching USD 8.9 billion by 2031. Asia-Pacific leads the market, accounting for 45% of the global share. Key metrics driving this growth include increasing demand for high-quality crops, soil nutrient depletion, and rising adoption of precision agriculture techniques.
The agricultural secondary nutrients market is gradually expanding, driven by rising demand for balanced crop nutrition to improve productivity and quality. Farmers are becoming more conscious of the relevance of secondary nutrients in crop growth, and there is an increasing demand for ecologically friendly agricultural approaches.
DOWNLOAD FREE SAMPLE
Market Trends:
The agricultural secondary nutrients market is rapidly shifting towards precision agriculture and customized nutrient management. Farmers are increasingly relying on technologies like soil testing, GPS-guided application systems, and data analytics to optimize secondary nutrient utilization. This approach enables the customized delivery of calcium, magnesium, and sulphur based on individual soil and crop requirements, resulting in increased nutrient utilization efficiency and less environmental impact. For example, farmers are increasingly using variable rate technology (VRT) to deliver secondary nutrients, allowing them to tailor application rates to individual field zones. Furthermore, slow- and controlled-release formulations of secondary nutrients are gaining popularity for ensuring consistent nutrient delivery throughout the crop growth cycle.
Market Segmentation:
Calcium dominates the agricultural secondary nutrients market, accounting for the largest share, due to its importance in plant cell wall synthesis, root development, and overall plant structure. Calcium is crucial for fruit and vegetable crops, especially in preventing diseases such as blossom end rot in tomatoes and bitter pit in apples.
Nano-calcium formulations are among the most recent advances in calcium supplementation. In 2023, several agrochemical businesses launched calcium solutions based on nanotechnology, which improve nutrient absorption and efficiency while resolving calcium immobility in plants. The calcium segment is predicted to grow at a 5.2% CAGR between 2024 and 2031, driven by rising demand for fruit and vegetable output and a growing preference for protected agriculture. In 2023, calcium-based solutions accounted for more than 40% of the global agricultural secondary nutrient market.
Market Key Players:
Prominent players in the agricultural secondary nutrients market include Nutrien Ltd., Yara International ASA, The Mosaic Company, K+S Aktiengesellschaft, ICL Group Ltd., Nufarm Limited, Koch Industries, Inc., Coromandel International Limited, Deepak Fertilisers and Petrochemicals Corporation Ltd., and UPL Limited. These companies are leading the market with their innovative approaches, extensive product portfolios, and robust distribution networks, continuously setting industry standards and driving market growth.
Contact Us:
Name: Hari Krishna
Email us: [email protected]
Website: https://aurorawaveintellects.com/
0 notes
Text
Growth and Outlook of the Fertilizer Market in Argentina: Trends, Challenges, and Forecast (2024-2032)

Argentina Fertilizer Market: Analysis and Growth Forecast (2024-2032)
In 2023, Argentina’s fertilizer market reached a volume of approximately 2.57 million tons, positioning itself as a key player in the global fertilizer sector. With a strong agricultural foundation, Argentina’s fertilizer industry plays an essential role in meeting the demand for agricultural productivity, particularly in key crops such as soybeans, corn, and wheat.
The fertilizer market in Argentina is expected to grow steadily during the forecast period from 2024 to 2032, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.80%. This growth trajectory is driven by several key factors, including increased agricultural output, a rising population that demands more food production, and the ongoing development of sustainable farming practices.
Factors Driving Growth
Agricultural Expansion and Crop Demand Argentina is one of the largest agricultural producers in the world, and its agricultural sector is continuously evolving. The demand for fertilizers is closely linked to the cultivation of key crops like soybeans, maize, and wheat, which are vital for both domestic consumption and export. Fertilizer use is integral to boosting crop yields and ensuring the continued success of the agricultural industry. As the demand for food and biofuels rises globally, so does the need for fertilizers to maintain and improve crop production.
Rising Adoption of Precision Agriculture Technological advances, such as precision farming, are becoming more popular in Argentina. This includes the use of advanced machinery, sensors, and data analytics to optimize fertilizer application. With precision agriculture, farmers can enhance productivity and reduce waste, further driving the demand for high-quality fertilizers. These innovations allow for more targeted and efficient use of fertilizers, contributing to both economic and environmental sustainability.
Export Demand Argentina is a leading exporter of agricultural products, and fertilizers are critical to maintaining the competitiveness of the country’s farming sector. Fertilizer demand is expected to remain strong due to export-oriented agricultural practices, especially for soybeans and cereals. As global food demand continues to rise, Argentina is expected to increase its export volume, further stimulating fertilizer usage.
Sustainability Trends In response to environmental concerns, Argentina is seeing a gradual shift toward sustainable farming practices. The use of bio-based fertilizers, organic amendments, and innovative solutions like slow-release fertilizers is gaining momentum. As environmental regulations become more stringent, and as consumer preferences lean toward eco-friendly agricultural products, the fertilizer market in Argentina is adapting to meet these challenges.
Government Support and Policy Initiatives The Argentine government has also shown support for the agricultural sector by providing incentives for the use of fertilizers and soil amendments. Initiatives aimed at enhancing soil fertility and improving agricultural sustainability will likely contribute to market growth. The government’s role in providing subsidies and promoting agricultural research further facilitates this development.
Market Segmentation
The Argentina fertilizer market is segmented into various categories based on the type of fertilizer, application methods, and crop types.
Fertilizer Types:
Nitrogen Fertilizers: The largest segment in the Argentine market, nitrogen fertilizers are primarily used to enhance crop yields by providing essential nutrients for plant growth.
Phosphatic Fertilizers: Phosphorous is critical for root development, and as such, phosphatic fertilizers are widely used for crops like wheat and corn.
Potash Fertilizers: Potash helps in the development of strong plant structures and is important for high-value crops.
Micronutrient Fertilizers: These fertilizers contain essential trace elements and are becoming increasingly important as farmers aim to optimize crop nutrition.
Application Methods:
Foliar Application: Increasing in popularity for delivering nutrients directly to plants through leaves.
Soil Application: The traditional method, where fertilizers are applied to the soil to supply nutrients.
Fertigation: Fertilizer is mixed with irrigation water and delivered to crops efficiently.
Crop Types:
Cereals & Grains: Corn, wheat, and barley are significant contributors to the fertilizer market in Argentina.
Oilseeds: Soybeans, the largest oilseed crop in Argentina, drives much of the fertilizer demand.
Fruits & Vegetables: Growing demand for diversified agricultural production leads to increased fertilizer usage in fruit and vegetable farming.
Challenges Facing the Fertilizer Market
Despite the positive growth prospects, the fertilizer market in Argentina faces some challenges. These include:
Price Volatility: Fertilizer prices are often influenced by global supply and demand, as well as geopolitical events. Price volatility can make it difficult for farmers to plan their budgets and for the industry to maintain stable growth.
Environmental Concerns: Excessive use of chemical fertilizers can lead to soil degradation and water contamination. There is a growing emphasis on promoting sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices, which may increase the demand for more expensive, eco-friendly fertilizers.
Logistics and Supply Chain Issues: The transportation and distribution of fertilizers in Argentina can sometimes be a challenge, particularly in rural areas. The country's infrastructure and logistics capabilities must be improved to keep up with the growing demand for fertilizers.
Market Forecast (2024-2032)
Over the forecast period from 2024 to 2032, the Argentina fertilizer market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 2.80%. This growth is supported by the continued demand for agricultural production, technological advancements in fertilizer application, and the shift toward sustainable farming practices. By 2032, the market is projected to reach a volume of approximately 3.31 million tons.
The demand for fertilizers will likely increase as Argentina seeks to maintain and enhance its agricultural output in the face of a growing global population and changing environmental conditions. Furthermore, the adoption of new farming technologies and the continued focus on export growth will play a crucial role in sustaining the market’s positive trajectory.
0 notes
Text

Global Primary Nutrient Fertilizers Market Size, Share, Growth and Forecast 2031
Global primary nutrient fertilizers market is projected to witness a CAGR of 7.20% during the forecast period 2024-2031, growing from USD 2.93 billion in 2023 to USD 5.10 billion in 2031. The market is highly significant toward achieving the ever-increasing demand for food globally. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (N-P-K) based fertilizers help boost soil health and increase crop production and crop yield. With the expansion of the global population, there is an incessant demand for food, and therefore farmers and agribusinesses are turning to the use of these fertilizers to enhance productivity, given the scarce arable lands available.
The market has a great advantage because of the constant ongoing developments, including improved nutrient use and reduced environmental pollution with the help of slow-release and controlled-release fertilizers. Sustainable farming practices and healthy soils are gaining momentum as farmers attempt to increase yield without compromising environmental stewardship.
In addition, companies are developing innovative machines for fertilizer application, boosting the demand for fertilizers in the market. For instance, in February 2024, the Brazilian multinational Grupo Jacto, which focuses on agricultural machinery, solutions, and services, introduced the Uniport 2024 NPK self-propelled fertilizer machine. The machine is remarkable for its design, characterized by an engine placed in front, a spacious operating area, and a tank of 8000 grams capacity. It is further equipped with a number of onboard technologies oriented towards environmental protection.
Nonetheless, there are issues, such as the volatility of the prices of raw materials and pollution due to excessive usage of fertilizers, which need to be addressed. The market has been changing with an increasing emphasis on cost-effectiveness, environmental sustainability, and customized offerings for different crops and regions. In general, the global primary nutrient fertilizers market is anticipated to grow owing to the increasing need for agriculture for the production of crops and eco-friendly farming methods.
Advancements in Fertilizer Technology to Catalyze Market Expansion
Improvements in fertilizer technologies are changing the scope of agriculture by enhancing medieval efficiency with methods currently practiced in a much more sustainable and precise way. With controlled-release and slow-release fertilizers, the nutrients are supplied synchronously with the rate of their uptake by plants to minimize the runoffs. Fertilizers in the form of nanoparticles, known as nano-fertilizers, boost the effectiveness of fertilization, increasing the range of its usage and lowering the chances of polluting the environment. Moreover, innovations in the form of fertilizer additives add to the advancements in the industry. For instance, in March 2023, Phospholutions Inc. launched its latest phosphate fertilizer technology, RhizoSorb, to assist in crop production in the United States. The patented fertilizer ingredient, RhizoSorb, works in a unique way to boost the effectiveness of phosphorus fertilizers. It is a fusion of activated metal oxides fixed directly into fertilizer granules during manufacturing.
Furthermore, in most irrigation systems, water-soluble fertilizers are common, making sure that precision application is used in high-valued crops and high yields. Moreover, there is a rise in the production of biostimulants and biofertilizers that are obtained from natural sources to improve soil quality and minimize the use of chemicals. These innovations help farmers to increase the level of their production in a responsible manner in order to sustain the growing demand for food worldwide.
Sustainable Farming Practices to Influence Market Growth
The goal of sustainable agriculture is to grow food that does not harm the environment, supports biodiversity, and does not consume the resources of the earth more than it can replenish for future generations. In this context, organic farming is an essential aspect as it refrains from the use of artificial chemicals and pesticides, relying instead on natural fertilizers, compost, and crop rotation to maintain soil quality while preventing erosion of the soil. Governments worldwide are promoting the concept of organic farming to align with global sustainability goals. In fact, according to a USDA study released in November 2023, in 2021, the total area of land in the United States that is certified organic reached 4.89 million acres. Over the last two decades, a higher amount of government spending has been approved for the USDA initiatives that enhance organic research. The mandatory spending cap for the Organic Agriculture Research and Extension Initiative has undergone enormous changes, from USD 3 million in the year 2002 to USD 50 million for the year 2023.
Other sustainable practices include the diversification of crops and the application of integrated pest management (IPM) techniques to minimize chemical usage and enhance the biological equilibrium. The incorporation of these methods leads to increased farm output and improved climate change resilience while striving to achieve high yields without compromising on environmental protection and soil health for the future.
Nitrogen-based Fertilizers Hold a Significant Market Share
The global fertilizers market is dominated by nitrogen-based fertilizers, which are important for increasing crop yield. The development of a plant cannot take place if nitrogen is absent since this is an important component for photosynthesis and protein synthesis, which are essential for the growth and translocation of nutrients in the plant. Most farmers use nitrogen fertilizers because of the nutrient’s quick effect on crop growth, especially for cereals and grains with high demand.
The ever-increasing need for nitrogen fertilizers is further driven by the global concern for food supply as they allow farmers to fully utilize the minimal cultivable land. However, the environmental issues associated with nitrogen leaching and emissions are leading to the emergence of controlled-release and precision application technologies that help to enhance productivity while ensuring the principles of sustainability are respected. For instance, in September 2024, Malaysia-based National Farmers’ Association (NAFAS) introduced its latest nitrogen-based controlled-release liquid fertilizer, Peladang 25, created to guarantee that its nitrogen content is released gradually, giving plants consistent and efficient nutrition throughout their growth stages. The fertilizer is suitable for crops such as oil palm, Napier grass, rice, and pineapple and is compatible with herbicides and fungicides.
North America to Dominate the Market Growth
North America is positioned at the forefront of the primary nutrient fertilizers market owing to the high level of development in agriculture and the wide use of sophisticated techniques for farming. This is mainly driven by large-scale agriculture practiced in the region that uses substantial fertilizers to improve crop production, especially in key crops such as corn, wheat, and soybeans. Advanced fertilizer technologies such as controlled released fertilizers and precision agriculture have been adopted in North America to maximize farm inputs and protect the environment from pollution associated with fertilizer use. Strengthening its position in the region, in June 2023, Everris International B.V. launched a new line of advanced foliar and fertigation products under the brand name Nova in North America. The objective is to provide high-quality water-soluble N-P-Ks and micronutrients to the crops. The range includes Nova FINISH, Nova PULSE, Nova ELEVATE, and Nova FLOW. These products primarily aim to bring the crop nutrients more efficiently to the intended site of action and are designed to achieve maximum solubility and good compatibility with most herbicides and crop protectants.
By encouraging the use of fertilizers and advances in sustainable agriculture practices, governmental backing and conducive agricultural policies come into play. Nevertheless, as awareness of environmental consequences rises, the North American market is progressively making a turn to organic fertilizers aiming at sustainability and environmental conservation without compromising agricultural efficiency.
Download Free Sample Report
Future Market Scenario (2024 – 2031F)
As the world’s population continues to rise, so will the demand for more efficient fertilizers to enhance agricultural production.
A better understanding of the quality of soil will enhance the demand for balanced soil nutrient applications as well as soil-friendly fertilizers.
It is anticipated that there will be a market for agrochemicals aimed at increasing the resilience of crops to extreme weather conditions.
Report Scope
“Primary Nutrient Fertilizers Market Assessment, Opportunities and Forecast, 2017-2031F”, is a comprehensive report by Markets and Data, providing in-depth analysis and qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current state of global primary nutrient fertilizers market, industry dynamics, and challenges. The report includes market size, segmental shares, growth trends, opportunities, and forecast between 2024 and 2031. Additionally, the report profiles the leading players in the industry, mentioning their respective market share, business models, competitive intelligence, etc.
Click here for full report- https://www.marketsandata.com/industry-reports/primary-nutrient-fertilizers-market
Latest reports-
Contact
Mr. Vivek Gupta 5741 Cleveland street, Suite 120, VA beach, VA, USA 23462 Tel: +1 (757) 343–3258 Email: [email protected] Website: https://www.marketsandata.com
0 notes
Text
Fertilizers Market-Industry Forecast, 2024–2030
Fertilizers Market Overview

Request Sample Report:
Fertilizers are substances added to soil or plants to enhance their growth and productivity by supplying essential nutrients. These nutrients include macronutrients like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), and micronutrients like iron, zinc, and magnesium, which are vital for plant development. Fertilizers are classified into organic (natural sources like manure and compost) and inorganic (chemically synthesized). They play a significant role in modern agriculture by increasing crop yields and ensuring food security
Report Coverage
The report: “Fertilizers Market — Forecast (2024–2030)”, by IndustryARC, covers an in-depth analysis of the following segments of the Fertilizers industry.
By Type: Organic Fertilizers, Inorganic Fertilizers, and Bio-Fertilizers.
By Form: Granules, Liquid, Gaseous and Others.
By Method of Application: Foliar Spraying, Fertigation, Sowing, Broadcasting, Spraying, Drip Method, and Others
By Application: Agriculture, Gardens, Sports Fields, and Others
By Crop Type: Horticulture Crops, Cash Crops, Cereals, Turfs and Ornamental Crops, Plantation Crops, and Others.
By Geography: North America, South America, Europe, APAC, and RoW.
However, the excessive use of fertilizers can harm the environment. Over-application may lead to soil degradation, water pollution through runoff, and the release of greenhouse gases. To minimize these effects, adopting sustainable practices like balanced fertilizer use, integrated nutrient management, and using slow-release formulations is crucial. This ensures agricultural productivity while maintaining environmental health.
Inquiry Before Buying :
Key Takeaways
Asia Pacific dominates the fertilizers market owing to rapid increase in food demand and agriculture industry.
The major technological innovations in the industry, along with growing demand for bio-based and micronutrient fertilizers, are expected to drive the market.
The market drivers and restraints have been assessed to understand their impact over the forecast period.
The report further identifies the key opportunities for growth while also detailing the key challenges and possible threats.
The other key areas of focus include the various applications and end-use industry in Fertilizers market and their specific segmented revenue.
Fertilizers Market Segment Analysis — By Type
Inorganic fertilizers held the largest share of more than 50% in the fertilizers market in 2020. Nutrient management is a key issue in sustainable soil fertility. The global supply of ammonia, phosphoric acid and potash is estimated at around 270 million tons from a total capacity of 310 to 315 million tons. Of all the regions, the demand for nitrogen fertilizers was the highest in the Americas, South Asia and Western Europe. Nevertheless, small supply surpassed demand in these markets. Chemical fertilizers face some risks from a health point of view. While it contributes to plant growth and improves yield, it shakes soil pH at the back of long-term use; repeated applications appear to lead to the build-up of toxic chemicals such as arsenic, cadmium and uranium in the soil; and the risk of over-use of fertilizers can disrupt the entire microbial environment, causing pests to rise and contribute to greenhouse gases.
Schedule a Call:
Fertilizers Market Segment Analysis — By Forms
Liquid held the largest share in the Fertilizers market in 2020. The liquid formulation held the largest share in the fertilizers market. The ease of application and transportation are the key drivers for the growth of the liquid formulations segment. Farmers have been using it for many years, as it is easy and safe to handle in comparison with dry formulation. With the increase in organic farming and increased acreages under precision irrigation technologies. They are adaptable to any type of sprayer, ranging from portable sprayers to hydraulic spraying machines. They are relatively easier to handle for treating large areas, which is the main reason for dominating the fertilizers market.
Fertilizers Market Segment Analysis — By Crop Type
Cereals held the largest share in the Fertilizers market in 2020 growing at a CAGR of 5.6%. Since cereals are grown in almost all countries, the global demand for insecticides is high for them. On a global level, the total cereal production has been increasing, and with the growth in cereal production and consumption, it has become important for producers to focus more on its yield and quality by using effective fertilizers. The cereals and grains are witnessing growth as they are a rich source of vitamins and minerals, and are used in large amounts in animal feed. The increase in demand for food and decline in arable land has prompted the increase in demand for fertilizers to meet the demand and reduce scarcity of foods. Therefore, farmers have been using fertilizers in combination with conventional chemicals, which has helped them in achieving no residue crops with internationally accepted standards. This factor will drive the growth of the fertilizers market in the forecast period.
Fertilizers Market Segment Analysis — By Geography
Asia-Pacific (APAC) dominated the Fertilizers market consisting market share of 42% in 2020 followed by North America and Europe. In Asia, rice is a large nitrogen-consuming crop. Due to growing concerns about the current pattern of use of fertilizers, heavy dependence on nitrogen fertilizers, poor nutritional management, lack of additional inputs, declining soil fertility, and weak marketing and distribution systems, all of these have emerged as major constraints to improve fertilizer efficiency in the region. These concerns have given way to biofertilizers and micronutrient fertilizers to grow and fuel the fertilizer market in the region. World markets are still suffering from the consequences of the Covid-19 pandemic that is sweeping the globe. The fertilizer sector has been affected from the outset, mainly in China, which is the largest producer and user of phosphates, sulphur and sulphuric acid, while Brazil and India will continue to do so.
Fertilizers Market Drivers
Growing uptake of Organic Fertilizer will drive the market.
The agriculture industry is limiting the use of chemical fertilizers and is gradually embracing organic and biofertilizers globally to encourage not only plant growth but also soil health. These are also referred to as “soil conditioners” made from plant or animal waste due to their capacity to retain water and nutrients for a long time. In addition, organic fertilizers are less harmful, quickly decomposed, reusable, safe and environmentally friendly and can be stored for a longer period of time due to their ability to withstand temperatures of up to 45 degrees Celsius or more.
Increasing R&D will augment the growth of Fertilizers.
Major fertilizer suppliers are increasing their R&D spending due to stringent regulations and product complexities since sales of fertilizer products vary depending on the climatic conditions and crop variance. In addition, leading suppliers are introducing newer technologies at their production plants in order to increase capacity and reduce production costs.
Fertilizers Market Challenges
Fluctuation in prices will hamper the market to growth.
The fertilizer prices of all three, including ammonia, DAP and potash, increased on the back of tight supply and strong demand in 2018 over different periods. In the third quarter of 2018, the prices of ammonia increased at the back of several plant changes, resulting in a tight supply. Further, potash prices remained firm in the second quarter of 2019 on the back of overall supply tightness. The current situation of fertilizers had indicated higher costs in 2019 as the production prices of ammonia, DAP and potash has increased in 2019.
Buy Now :
Strict Regulations can restrict market growth.
Fertilizers produce hazardous waste and EPA guidelines set limits for the amounts of heavy metals and other harmful compounds that may be found in fertilizer products. These concentration limits are based on the best demonstrated available technology to reduce the toxicity and mobility of hazardous constituents. In U.S the regulations on the use of hazardous waste in fertilizers may be stricter than the Federal guidelines, because regulations that are more stringent and/or wider in scope than the Federal regulations may be implemented by States.
Fertilizers Market Landscape
Technology launches, acquisitions and R&D activities are key strategies adopted by players in the Fertilizers market. In 2020 the Fertilizers market has been consolidated by the top five players accounting for xx% of the share. Major players in the Fertilizers market are Yara International ASA, The Mosaic Company, Nutrien Limited, K+S AG, Bayer, and Groupe OCP, among others.
Acquisitions/Technology Launches/ Product Launches
In November 2017, Yara International has acquired Agronomic Technology Corp (ATC). The acquisition has expanded the product portfolio of Yara International as well as strengthened its global presence.
In April 2019, Huber Engineered Materials acquired Miller Chemical & Fertilizer, LLC. Miller manufactures and distributes crop protection and nutritional agrichemical products designed to improve plant and crop production quality and yield. Miller sells its products into the farming and agricultural industries in more than 90 countries via its global sales force of skilled agronomists and distributors and targets the high-value segment of fruits, nuts and vegetables. The acquisition has strengthened the product portfolio of Huber Engineered Materials and its global outreach.
Key Market Players:
The Top 5 companies in the Fertilizers Market are:
CF Industries
Israel Chemicals Ltd
Nutrien Limited
The Mosaic Company
Yara International
For more Agriculture Market reports, please click here
0 notes
Text
Urea Fertilizer Manufacturers: Driving Agricultural Growth
Urea fertilizer manufacturer play a pivotal role in global agriculture by producing one of the most essential nitrogen-based fertilizers. Urea, with its high nitrogen content (46%), supports healthy plant growth and increased crop yields, making it indispensable for farmers worldwide. Understanding the operations, innovations, and impact of urea fertilizer manufacturers highlights their importance in ensuring food security and sustainable farming practices.
Manufacturing Process of Urea Fertilizer
The production of urea involves synthesizing ammonia and carbon dioxide under high pressure and temperature to form ammonium carbamate, which is then dehydrated to produce urea. The result is a highly concentrated nitrogen compound that is processed into prilled or granular forms suitable for agricultural use.
Manufacturers focus on achieving high efficiency and low environmental impact during production. Many employ advanced technologies to reduce energy consumption and emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Key Players in Urea Manufacturing
The global urea fertilizer market is dominated by major manufacturers such as Yara International, CF Industries, and Nutrien. These companies operate large-scale facilities with state-of-the-art technology to meet the growing demand. In addition to multinational giants, smaller regional manufacturers cater to local markets, ensuring availability and affordability for farmers.
Innovations in Urea Manufacturing
Manufacturers are continuously innovating to enhance product quality and efficiency. Innovations include:
Coated Urea: Slow-release or controlled-release urea coatings reduce nitrogen losses and improve nutrient uptake by crops.
Eco-Friendly Production: Companies are adopting cleaner production methods, such as carbon capture technologies, to minimize environmental impact.
Custom Blends: Manufacturers often produce urea-based fertilizers blended with other nutrients to meet specific soil and crop needs.
Challenges and Opportunities
Urea manufacturers face challenges such as fluctuating raw material costs (particularly natural gas), stringent environmental regulations, and logistical issues. However, these challenges also drive opportunities for innovation, such as the development of alternative energy sources and sustainable production methods.
Importance to Agriculture
By producing high-quality urea fertilizer, manufacturers contribute significantly to global food production. Their efforts support farmers in achieving higher yields while promoting efficient resource use.
urea fertilizer manufacturer are essential players in agriculture. Through innovation, sustainability, and dedication to quality, they ensure a reliable supply of this critical agricultural input, helping to meet the demands of a growing global population.
0 notes
Text
Water and Soil Conservation: A Vital Approach for Sustainable Ecosystems
Water and soil are two of the most essential natural resources, fundamental to supporting plant life, agricultural productivity, and environmental health. However, unsustainable practices, climate change, deforestation, and urbanization have accelerated soil degradation and water scarcity globally. Soil erosion, water pollution, and depletion of groundwater supplies threaten food security, biodiversity, and human health. Water and soil conservation has therefore become crucial for maintaining ecosystems, supporting agriculture, and sustaining human life.
Why Water and Soil Conservation Is Important
Prevention of Soil Erosion: Soil erosion is one of the primary causes of land degradation. It reduces soil fertility, which in turn affects agricultural productivity. Conserving soil helps maintain its structure, nutrients, and organic matter, making it productive for longer periods.
Mitigation of Water Scarcity: Water scarcity affects nearly half of the world's population. Overuse of water resources for agriculture, industry, and domestic use has led to depleted water tables and river systems. Conservation helps manage this critical resource sustainably, reducing waste and promoting efficient usage.
Protection of Biodiversity: Soil and water conservation creates favorable conditions for various species to thrive, helping to maintain biodiversity. Healthy soils support a rich ecosystem of organisms, while clean water bodies sustain aquatic life and terrestrial animals relying on those water sources.
Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation: Soils store vast amounts of carbon, and soil conservation can prevent the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change. Moreover, healthy soil can retain more water, reducing the impact of droughts and flooding.
Key Water and Soil Conservation Techniques
1. Afforestation and Reforestation
Objective: To increase vegetation cover to prevent soil erosion and improve water retention.
Approach: Planting trees on degraded lands or replanting in deforested areas stabilizes soil with roots, absorbs excess water, and reduces runoff, which can lead to erosion.
2. Terracing
Objective: Reduce soil erosion on hilly terrains.
Approach: Terracing involves creating stepped levels on a slope to slow water flow, reduce runoff, and allow water to seep into the ground, which helps prevent erosion and improve water availability for crops.
3. Contour Farming
Objective: Enhance water absorption and reduce erosion.
Approach: Farmers plow across slopes rather than down them, following the natural contour of the land. This technique reduces the speed of water flow, allowing more water to be absorbed into the soil and decreasing soil erosion.
4. Rainwater Harvesting
Objective: Capture and store rainwater to reduce dependence on groundwater.
Approach: Rainwater harvesting techniques such as rooftop collection, bunds, and ponds collect rainfall and channel it into storage for future use. This water can be used for irrigation, groundwater recharge, or domestic purposes.
5. Crop Rotation and Cover Cropping
Objective: Improve soil health, reduce erosion, and increase water retention.
Approach: Rotating crops and using cover crops like clover and legumes help prevent soil exhaustion and erosion. These crops provide ground cover, which reduces water runoff and enhances soil fertility by replenishing nutrients.
6. Mulching
Objective: Conserve moisture, reduce erosion, and improve soil fertility.
Approach: Applying a layer of organic or inorganic material on the soil surface protects it from erosion and evaporation. Mulching maintains soil temperature, reduces weed growth, and adds organic matter to the soil as it decomposes.
Benefits of Water and Soil Conservation
Enhanced Agricultural Productivity: Healthy soils support robust plant growth, leading to increased crop yields. By conserving water, farmers can manage water resources more efficiently, reducing the risk of crop failures.
Increased Resilience to Climate Change: Conservation techniques such as rainwater harvesting and terracing can help communities adapt to changing rainfall patterns and extreme weather events, making agricultural systems more resilient.
Improved Water Quality: Reducing soil erosion decreases sedimentation in water bodies, which can reduce pollution levels and improve water quality for drinking, recreation, and habitat for aquatic life.
Long-term Economic Benefits: Water and soil conservation can reduce costs associated with fertilizers, pesticides, and other farming inputs, resulting in financial savings for farmers and communities.
Preservation of Ecosystems: Conservation practices promote biodiversity by creating healthier ecosystems that support a wider variety of plant, animal, and microbial life.

Community Involvement in Conservation
Local communities play a pivotal role in water and soil conservation. Community-based programs such as watershed management, communal rainwater harvesting, and education on sustainable farming practices empower local populations to take ownership of conservation efforts. Collaboration with governmental and non-governmental organizations can further improve outcomes by providing technical support, resources, and knowledge.
The Role of Government and Policy
Governments can help promote water and soil conservation through:
Policy Incentives: Subsidies, grants, and low-interest loans for conservation initiatives make it easier for farmers and businesses to adopt sustainable practices.
Research and Development: Investing in research can lead to improved, locally adaptable conservation techniques.
Public Awareness Campaigns: Raising awareness about the importance of conserving natural resources can encourage people to adopt sustainable practices in their daily lives.
Conclusion
Water and soil conservation is crucial for sustainable development, environmental protection, and climate change mitigation. Effective conservation efforts require a holistic approach that integrates community participation, scientific research, government policy, and sustainable agricultural practices. Protecting these resources today is an investment in a healthier, more resilient ecosystem that can meet the needs of future generations. By committing to these practices, we can ensure that our soil remains fertile and our water remains abundant, supporting life and livelihoods for years to come.
Also read about Jalyukt Shivar Abhiyan 2.0, A project dedicated to water conservation.
0 notes
Text
Cognitive and Stress-Enhancing Supplements: Unlocking Mental Clarity with Nature
In today’s fast-paced world, the need for cognitive enhancement and stress management has never been more crucial. Whether you’re a professional trying to stay sharp, a student looking to improve focus, or simply someone aiming to manage everyday stress more effectively, supplements that boost brain function and mitigate stress are becoming go-to solutions. These supplements offer natural ways to sharpen cognitive abilities and foster mental resilience. At the forefront of this revolution in wellness is Glucorp Industry, which combines ethical practices with innovative health products, including cognitive and stress-enhancing supplements.

The Power of Cognitive and Stress-Enhancing Supplements
Supplements aimed at cognitive and stress enhancement often contain ingredients known for their neuroprotective and adaptogenic properties. These natural compounds not only help improve focus, memory, and mental clarity but also support stress reduction by balancing cortisol levels. Ingredients like ashwagandha, ginseng, omega-3 fatty acids, and L-theanine are commonly found in such supplements. But the latest innovations are also focusing on using sustainable, plant-based ingredients, tapping into nature’s bounty to provide holistic health benefits.
Among these new developments, Brown Rice Syrup has emerged as a vital ingredient in the creation of supplements that target both cognitive enhancement and stress reduction. Known for its natural sweetness and low glycemic index, Brown Rice Syrup serves as an excellent natural alternative to processed sugars, making it ideal for those looking to maintain balanced energy levels without the spikes and crashes associated with refined sugars. But beyond its energy-boosting properties, this natural syrup plays a unique role in stress relief by maintaining steady glucose levels, supporting brain function, and helping manage mental fatigue.
Glucorp Industry’s Role in Cognitive and Stress-Enhancing Supplements
Glucorp Industry has long been dedicated to promoting sustainable and ethical health solutions. As part of its commitment to developing cutting-edge supplements, Glucorp has delved into creating products that enhance cognitive function while reducing stress. By focusing on organic and plant-based ingredients, Glucorp ensures that its supplements are free from harmful chemicals, making them safe for everyday use.
One of the key innovations from Glucorp Industry is the use of Brown Rice Syrup in its supplements. Not only does Brown Rice Syrup act as a natural sweetener, but it also enhances energy levels, providing a slow and steady release of glucose, which is essential for maintaining mental clarity. The balanced energy output prevents mental fatigue, allowing individuals to stay sharp and focused for longer periods. Moreover, by regulating glucose levels, Brown Rice Syrup plays an essential role in mitigating stress, making it an ideal ingredient in Glucorp's cognitive and stress-relief formulas.
Glucorp’s supplements are also enriched with adaptogens like Rhodiola Rosea and Ashwagandha, which are known for their ability to lower cortisol levels and improve the body’s response to stress. Combined with the stable energy release from Brown Rice Syrup, these supplements not only enhance brain function but also provide a natural defense against the physical and mental toll of stress.
Brown Rice Syrup: A Sustainable and Nutritious Ingredient
Beyond its benefits for cognitive and stress management, Brown Rice Syrup is a key component of Glucorp Industry’s commitment to sustainability. Derived from whole grains, Brown Rice Syrup is a healthier and environmentally friendly alternative to artificial sweeteners and high-fructose corn syrup. Its production involves minimal processing, retaining more of the rice’s natural nutrients, making it a nutrient-rich addition to any supplement.
As a renewable and biodegradable ingredient, Brown Rice Syrup aligns perfectly with Glucorp’s mission to provide health solutions that do not harm the environment. By choosing Brown Rice Syrup as a core ingredient, Glucorp not only ensures the best nutritional benefits for its consumers but also helps reduce the carbon footprint associated with more heavily processed alternatives.
Conclusion: Enhancing Brain Function and Reducing Stress with Nature
As we look for natural ways to support our cognitive health and manage stress, supplements that are rooted in organic and plant-based ingredients are leading the charge. Glucorp Industry’s focus on developing supplements with ingredients like Brown Rice Syrup demonstrates how innovation and sustainability can go hand-in-hand. By enhancing cognitive function, regulating energy, and promoting stress relief, Glucorp's supplements provide a natural, effective, and ethical solution for those seeking mental clarity and balance.
Incorporating Brown Rice Syrup into your daily regimen may be just the key to unlocking better brain health and stress management, all while supporting a sustainable future. With Glucorp at the helm of this wellness revolution, the future of cognitive and stress-enhancing supplements looks brighter—and greener—than ever before.
0 notes
Text
Bentonite Granules: Versatile Solutions for Agriculture and Industry
Bentonite granules are derived from bentonite clay, a naturally occurring mineral formed from volcanic ash. The granules are typically processed to create uniform, small particles that are easy to handle and apply. There are two main types of bentonite clay: sodium bentonite and calcium bentonite. Sodium bentonite is known for its superior swelling and absorption capabilities, while calcium bentonite is prized for its binding and sealing properties.
These granules are widely used in various industries because of their ability to absorb water, retain moisture, and enhance soil properties, making them ideal for both agricultural and industrial applications.

Key Benefits of Bentonite Granules
1. High Absorption Capacity
One of the standout features of bentonite granules is their high absorption capacity. Sodium bentonite, in particular, can absorb several times its weight in water, which makes it extremely useful in moisture retention applications. This property is vital in agriculture, where maintaining soil moisture is essential for crop growth and overall yield.
2. Soil Conditioning
In agriculture, bentonite granules are commonly used as soil conditioners. They improve soil texture, aeration, and moisture retention, which are crucial factors for crop productivity. By using bentonite granules, farmers can enhance the quality of their soil, promote root development, and improve plant growth. Bentonite also helps to prevent soil erosion by increasing the soil's water retention capacity.
3. Eco-Friendly and Natural
Bentonite is a natural and eco-friendly material, making it an excellent choice for environmentally-conscious applications. It does not introduce harmful chemicals into the environment and is safe to use in both agricultural and industrial settings. The eco-friendly nature of bentonite granules makes them a sustainable option for improving soil and managing water retention in various applications.
Applications of Bentonite Granules
1. Agriculture
In agriculture, bentonite granules are widely used as soil conditioners and carriers for fertilizers and pesticides. Their ability to absorb and retain water helps improve soil fertility and enhance crop growth. Additionally, they are often used to bind fertilizers and pesticides, ensuring even distribution of these substances across fields.
The slow release of nutrients from fertilizers bonded with bentonite granules enhances the effectiveness of fertilizers and reduces the risk of nutrient runoff, making it a cost-effective solution for farmers. This property ensures long-term soil health and higher crop yields.
2. Animal Feed
Bentonite granules also play a role in animal feed. They are used as binders to improve the texture of animal feed and help in the digestion process. Bentonite helps absorb toxins in animal feed, ensuring that livestock consumes healthy and nutrient-rich diets. This contributes to overall better health and performance in animals.
3. Industrial Applications
In industries, bentonite granules are used in various processes, including drilling, water treatment, and even construction. The absorption and swelling properties of sodium bentonite are utilized in drilling fluids to cool and lubricate drilling equipment while stabilizing boreholes. In construction, bentonite granules are used to seal ponds, landfills, and other containment areas, preventing water leakage.
Additionally, bentonite granules are used in water treatment to remove impurities. Their ability to absorb contaminants makes them an efficient material for treating industrial wastewater and ensuring cleaner, safer water.
4. Pond Lining and Sealing
Sodium bentonite granules are a popular choice for lining and sealing ponds, dams, and other water bodies. The granules form a waterproof barrier by swelling and sealing any cracks or gaps in the soil, preventing water from seeping through. This natural and cost-effective solution ensures long-lasting water retention without the need for artificial liners.
How to Choose the Right Bentonite Granules
When selecting bentonite granules for your specific application, consider the following factors:
Type of Bentonite: Sodium bentonite is ideal for applications requiring high absorption and swelling, such as pond sealing and drilling. Calcium bentonite is better suited for applications that require binding and sealing, such as in construction or fertilizers.
Particle Size: The size of the bentonite granules can impact their effectiveness. Finer granules are better for applications like soil conditioning and pesticide binding, while larger granules may be more effective in construction or water treatment.
Purity and Quality: Always work with reliable bentonite granules manufacturers that provide high-quality products. Ensuring the granules are free of impurities and meet industry standards will guarantee the best results for your application.
Conclusion
Bentonite granules offer a wide range of benefits for industries ranging from agriculture to construction. Their natural properties, such as high absorption, water retention, and soil conditioning capabilities, make them a valuable resource for numerous applications. Whether you’re looking to enhance soil quality, seal a pond, or treat industrial wastewater, bentonite granules provide efficient and eco-friendly solutions.
At Amrfeo, we are dedicated to providing high-quality bentonite granules that meet the needs of various industries. With a focus on quality and performance, Amrfeo ensures that our bentonite products deliver optimal results for your specific applications. Trust Amrfeo for reliable and eco-friendly bentonite solutions that enhance your operations and projects.
0 notes
Text
Bupleurum special fertilizer: fertilizer production machines can deliver good results
In the field of Chinese herbal medicine cultivation, bupleurum is an important medicinal plant, and its quality and yield are very important for the development of Chinese medicine industry. The emergence of special fertilizer for bupleurum provides precise nutritional support for the growth of bupleurum. Behind this, fertilizer production machines play an indispensable role.

Into the production workshop of bupleuri special fertilizer, a variety of advanced fertilizer production machines are eye-catching. In the raw material preparation stage, high-precision measuring equipment will weigh and transport various raw materials in precise proportions. These raw materials include high-quality nitrogen fertilizer, phosphate fertilizer, potassium fertilizer, organic fertilizer, microbial strains and so on. The accuracy of the measuring equipment is directly related to the accuracy of the fertilizer formula, ensuring that each batch of bupleurum special fertilizer can meet the nutritional needs of bupleurum.
Mixing equipment is one of the core machines in the production of special bupleurum fertilizer. It thoroughly mixes different raw materials so that various nutrients are evenly distributed in the fertilizer. The advanced mixing equipment uses a special mixing structure and control system to achieve an efficient and uniform mixing effect in a short time.
In the production process, some special fertilizer production machines may also be used. For example, to improve the biological activity and sustainability of fertilizers, beneficial microbial strains can be added. This requires the use of microbial culture and inoculation equipment to ensure the activity and number of microbial strains. At the same time, in order to meet the nutritional needs of bupleurum in different growth stages, slow-release technology can also be used, which requires the use of slow-release fertilizer production equipment, so that the fertilizer can slowly release nutrients and extend the action time of the fertilizer.
Packaging equipment is also an important part of the production of bupleuri fertilizer. It will produce good bupleuri special fertilizer for packaging for sale and transportation. Packaging equipment can be automatically packaged according to different specifications and requirements to improve production efficiency and packaging quality.
In the production enterprises of bupleurum special fertilizer, the efficient cooperative work of fertilizer production machines makes the production process of bupleurum special fertilizer scientific, standardized and efficient. From the preparation of raw materials to the packaging of finished products, every link has undergone strict quality control to ensure that the special bupleurum fertilizer produced has excellent quality and efficient fertilizer efficiency.
0 notes
Text
Organic Fertilizers: Nature's Way of Improving Soil Quality
Organic fertilizers refer to fertilizers derived from either plant or animal materials. They are produced by decomposing biomass of plants and animals to be used as fertilizer. Natural fertilizers enrich the soil with nutrients in a slow, steady release form to provide continuous nourishment to plants. They differ from conventional synthetic fertilizers in their mode of action and impact on soil health. Benefits of Organic Fertilizers Improves Soil Structure: Regular use of natural fertilizers improves the tilth and structure of soil. They increase the water holding and drainage capacity of soil. Organic matter acts as a glue, binding soil particles into aggregates. This improves aeration and promotes healthy root development. Supplies Micronutrients: Along with primary macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, natural fertilizers also supply micronutrients like iron, manganese, zinc, copper etc. which are essential for plant growth and nutritional quality of produce. They maintain the right balance of nutrients in soil. Enhances Soil Biology: Natural fertilizers add carbon to the soil in the form of humus which serve as food for myriad soil microorganisms. Organic Fertilizer It stimulates the activities of microflora and microfauna such as bacteria, fungi, earthworms etc. that play a vital role in nutrient cycling,decomposition of organic matter and disease suppression. Provides Slow-Release Nutrition: Nutrients from natural fertilizers are slowly and continuously released over a long period, matching the nutrient requirement of crops. This prevents losses due to leaching and maintains productivity. Synthetic fertilizers rapidly release salts that can burn roots if misapplied. Builds Soil Organic Matter: Regular application of organic residue enhances the soil organic matter levels which has a positive cascading impact on soil health, structure, water holding capacity and nutrient availability to plants. Soils rich in organic matter act as carbon sink and sequester greenhouse gases from atmosphere. Types of Organic Fertilizers Compost Manure: Compost manure is made from decomposition of plant and animal residues and waste in the presence of air under controlled conditions. It provides stabilized organic matter and nutrients in balanced form to soil. Well-decomposed compost improves soil aggregation and texture. Vermicompost: Vermicompost or worm compost produced through worm cultivation is an odorless, nutritious organic manure rich in humus, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and micronutrients. It has excellent water holding capacity and improves drainage in heavy soils. Green Manure: Green manuring involves growing green leafy crops or legumes and incorporating them back into soil when they are at flowering/podding stage. It enriches soil nitrogen content, supports beneficial microbes and leaves organic residues to add to soil structure. Bone Meal: Finely ground bone meal is a rich source of phosphate, calcium and other micronutrients required for overall plant growth. It is an excellent natural fertilizer for flowering and fruiting crops where phosphorus levels need to be maintained in soil. Biofertilizers: Biofertilizers contain living microorganisms which have an ability to convert atmospheric or applied elemental nutrients into forms easily assimilated by plants. Common biofertilizers are Rhizobium, Azotobacter, Azospirillum and blue-green algae.
Get more insights on Organic Fertilizers
Identify the language that you favour
French
German
Italian
Russian
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Portuguese
About Author:
Money Singh is a seasoned content writer with over four years of experience in the market research sector. Her expertise spans various industries, including food and beverages, biotechnology, chemical and materials, defense and aerospace, consumer goods, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/money-singh-590844163)
#Organic Fertilizers#Sustainable Agriculture#Natural Fertilizers#Organic Farming#Soil Health#Eco-Friendly Fertilizers#Composting#Organic Gardening
1 note
·
View note
Text
I wrote this report on glyphosate's effect on soil to send to my brother who's been spraying it on his deer garden. If anyone else would like to nerd out, check this out.💚 Sorry this has absolutely nothing to do with stripping.
I consulted with my teachers from the native plant conference that I recently attended, as well as chat gpt to find this information. I learned a lot myself in the process of researching this. Thanks for giving me the opportunity to totally nerd out! Let me know if you have any questions.
How does glyphosate work as an herbicide? It targets and inhibits a specific enzyme known as EPSPS, which is essential for plant growth. By disrupting amino acid production, glyphosate interferes with the shikimate pathway, a metabolic pathway present in plants, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. This pathway does not exist in mammals, making glyphosate’s action highly selective and contributing to its relative safety for animals. Glyphosate is systemic, meaning it is absorbed by the plant's leaves and then transported throughout the plant via its vascular tissue. This systemic nature makes glyphosate highly effective at killing perennial plants, as it ensures even distribution, preventing any part of the plant from surviving. Plants treated with glyphosate typically die within 1–3 weeks. Additionally, glyphosate binds tightly to soil particles, reducing its mobility and potential environmental impact. It is eventually broken down by soil microbes into harmless substances such as carbon dioxide, water, and phosphate.
What effect does glyphosate have on non-animal organisms like fungi and bacteria? Glyphosate can alter the composition and diversity of soil bacterial communities. Some studies suggest that it may inhibit certain beneficial bacteria, such as those involved in nitrogen fixation (e.g., Rhizobium), while potentially promoting the growth of others, including some opportunistic pathogens. Glyphosate can also impact the availability of nutrients and organic matter in the soil by affecting plant growth, which in turn influences the bacterial communities that depend on these nutrients. Saprophytic fungi, which decompose organic matter, may be particularly affected by glyphosate, as their activity can be reduced, slowing down decomposition processes and nutrient cycling, including nitrogen fixation, in the soil. Glyphosate can inhibit the growth of fungal hyphae, reducing the overall spread and development of the mycelium. This can impact the ability of fungi to colonize, decompose organic matter, and form symbiotic relationships with plants. Repeated or high levels of glyphosate application can lead to long-term changes in fungal communities, potentially reducing the abundance and diversity of beneficial fungi, including those that form extensive mycelial networks essential for soil health.
Why does that matter?
Bacteria are the primary decomposers in soil, breaking down complex organic materials into simpler ones that can be utilized by plants and other organisms. This process helps release essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon, into the soil. Certain bacteria can convert atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) into forms that plants can use, such as ammonia (NH₃). This process, known as nitrogen fixation, is vital for plant growth, as nitrogen is a key component of proteins and nucleic acids. Biological nitrogen fixation, which accounts for the vast majority of natural nitrogen fixation, relies entirely on the involvement of specific nitrogen-fixing microbes. These microbes play a crucial role in making nitrogen available to plants, thereby supporting plant growth and ecosystem productivity. When these microbes are unable to perform as nitrogen fixers, farmers are forced to add industrial nitrogen which is produced in chemical plants through a very environmentally taxing process. This is known as the Haber-Bosch process and is so hard on the environment because of the vast amounts of fossil fuels needed to produce it and the effects on aquatic life from its application (see: eutrophication, marine dead zones, and nitrate contamination of drinking water supplies).
Additionally, bacteria contribute to soil formation by producing sticky substances that help bind soil particles into aggregates. These aggregates improve soil structure by creating pore spaces that enhance water infiltration, root penetration, and air exchange. Some soil bacteria, such as those in the genus Bacillus and Pseudomonas, produce antibiotics and other compounds that inhibit the growth of pathogenic microbes. By outcompeting harmful organisms or directly killing them, these bacteria help protect plants from diseases.
Fungi play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter and are even more efficient at this process than bacteria. Mycorrhizal fungi form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, extending their hyphae—thread-like, tubular structures that are the basic building blocks of fungi—into the soil, and their mycelium—a dense, collective network of hyphae—into the plants themselves. This relationship increases the surface area for nutrient absorption, particularly phosphorus, and enhances the plant’s ability to access water and nutrients. In return, the plant supplies the fungi with carbohydrates. Mushrooms, the reproductive structures produced by mycelium, are part of this complex network. Beyond nutrient uptake, mycorrhizal fungi can also protect plants by outcompeting or directly suppressing soil-borne pathogens through the production of defensive compounds
Soil health is very dependent on the health of bacteria and fungi. The breakdown of organic matter by bacteria and fungi leads to the formation of humus, a stable, organic component of soil that enhances its fertility, water retention, and structure. Humus is essential for long-term soil health and productivity. The activities of bacteria and fungi help in sequestering carbon in the soil, either through the formation of stable organic matter or by fostering the conditions that lead to the long-term storage of carbon. Which is super cool because this basically reverses some of the effects of our emission producing activity. This can slowly increase the purity and quality of the surrounding air and water supplies by filtering out carbon and other contaminants such as heavy metals.
Earthworms play a vital role in maintaining soil health by aerating the soil, decomposing organic matter, and promoting nutrient cycling. Studies on the effects of glyphosate on earthworms have shown mixed results. Some research suggests that glyphosate can negatively impact earthworm populations by affecting their growth, reproduction, and overall activity. Exposure to glyphosate may cause earthworms to experience reduced weight, delayed maturation, and lower reproductive rates. Additionally, glyphosate can alter the microbial communities in the soil, which may indirectly affect earthworms by changing the availability of their food sources. However, the extent of these effects can vary depending on factors such as soil type, glyphosate concentration, and environmental conditions. While earthworms may survive glyphosate exposure, the potential sublethal effects could impact their long-term health and the ecosystem functions they support.
Summary: Glyphosate can have various effects on soil bacteria, fungi, and mycelium, ranging from inhibiting growth and altering community composition to disrupting essential microbial processes like decomposition and nitrogen fixing. The specific impacts depend on the concentration of glyphosate, soil characteristics, and the resilience of the microbial communities involved. While some effects may be short-term, repeated or high-dose applications of glyphosate can lead to longer-lasting changes in soil health and microbial diversity.
Pollinator Health
Glyphosate, while not acutely toxic to pollinators, can have significant sublethal and indirect effects. These include behavioral changes, disruption of gut microbiomes, and reproductive issues in bees, as well as the reduction of floral resources and habitat loss, which are critical for the survival of pollinators. The overall impact of glyphosate on pollinators is complex and can be exacerbated by interactions with other environmental stressors.
Behavioral Health: Some studies have shown that glyphosate exposure can affect the behavior of pollinators, particularly bees. For example, glyphosate can impair honeybee navigation, learning, and memory, which can reduce their ability to forage effectively and return to the hive.
Reproduction and Development: Glyphosate exposure has been associated with potential negative effects on the reproduction and development of bees. In some studies, glyphosate-exposed queen bees produced fewer offspring, and larval development was negatively impacted, potentially leading to weaker colonies.
Gut Microbiome: Glyphosate has been shown to disrupt the gut microbiome of bees. The gut microbiome is crucial for digestion, immunity, and overall health. Disruption of these microbial communities can make bees more susceptible to diseases and reduce their ability to detoxify pesticides.
Reduction in Floral Resources: Glyphosate is highly effective at killing a wide range of plants, including many wildflowers and weeds that are important food sources for pollinators. By reducing the availability of nectar and pollen, glyphosate can indirectly contribute to the decline of pollinator populations.The widespread use of glyphosate in agriculture, particularly in conjunction with glyphosate-resistant genetically modified crops, has led to large-scale monocultures. This reduces the diversity of plant species in the landscape, leading to a loss of habitat and food resources for pollinators.
Alternatives and Resources
Vinegar (Acetic Acid): Lowers the pH of plant tissues, causing them to dry out and die. Use: Often used in organic farming; effective against young, tender weeds but less so on established ones.
Cover Crops: Planting cover crops (e.g., clover, rye, alfalfa) can suppress weed growth by outcompeting weeds for sunlight, water, and nutrients. Use: Often integrated into crop rotation systems; also improves soil health.
***Mulching: Applying organic material (e.g., straw, wood chips) can prevent weed seeds from germinating by blocking light. Use: Common in gardening, landscaping, and organic farming; also helps conserve soil moisture and sequestered carbon.
Ruth Stout "Mulch Queen" Interview: https://m.youtube.com/watch?v=FB5_NmqTOm8
Texas A&M agri center mulching info: https://agrilifetoday.tamu.edu/2021/03/26/how-to-manage-garden-weeds-with-mulch/
Biological Control Agents: Examples: Insects, fungi, or bacteria that target specific weeds (e.g., Puccinia chondrillina, a rust fungus used against skeleton weed). Use: These agents can be effective in controlling specific weed species but usually require careful management.
Example: https://harpebio.com
***Solarization: Using clear (or opaque, such as a tarp) plastic to cover the soil, trapping solar heat to kill weed seeds and seedlings. Use: Typically used in warm climates; effective for preparing seedbeds or managing weeds in small plots.
Duration: Leave the plastic or tarp over the area for about a week of mostly sunny days. https://extension.umn.edu/planting-and-growing-guides/solarization-occultation
Crop Rotation: Changing the types of crops grown in a field each season to disrupt weed life cycles. Use: A key practice in integrated pest management (IPM); helps reduce weed pressure over time. https://ipm.ucanr.edu/what-is-ipm/
Integrated Weed Management (IWM): combines chemical, biological, mechanical, and cultural practices to manage weeds in a sustainable way. The goal is to reduce reliance on any single method, such as glyphosate, and instead use a diverse set of strategies to control weeds effectively. https://growiwm.org/what-is-integrated-weed-management/
Impact on Humans
Bayer has paid over $11 billion in settlements related to glyphosate litigation to date, with additional funds set aside for future claims. The total cost may rise as ongoing and future cases are resolved. The legal battles primarily revolve around allegations that glyphosate-based products cause cancer, specifically non-Hodgkin lymphoma, a claim that Bayer continues to dispute. Although reproductive health claims are not as prominent in the lawsuits, some studies suggest that glyphosate could interfere with the human endocrine system. Therefore, caution is advised, particularly for populations with high exposure levels, such as agricultural workers, to prevent potential reproductive harm from glyphosate exposure.
Additional Resources
Web articles:
*****Glyphosate: Its Environmental Persistence and Impact on Crop Health and Nutrition https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6918143/
The Impact of Glyphosate on Soil Health https://www.soilassociation.org/media/7202/glyphosate-and-soil-health-full-report.pdf
Glyphosate: Cancer and other health concerns
Removal of glyphosate from global usage: A Statement by the FIGO (International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics) Committee on Reproductive and Developmental Environmental Health
Glyphosate impairs aversive learning in bumblebees
Books:
The Complete Guide to Restoring Your Soil: Improve Water Retention and Infiltration; Support Microorganisms and Other Soil Life; Capture More ... Cover Crops, and Carbon-Based Soil Amendments by Dale Strickler
The Intelligent Gardener: Growing Nutrient-Dense Food by Steve Solomon
Whew, okay, that's all I got for ya. Take care and have a good week.
Love,
S
1 note
·
View note
Text

Global Secondary Macronutrient Fertilizers Market Size, Share, Growth and Forecast 2031
Global secondary macronutrient fertilizers market is projected to witness a CAGR of 4.72% during the forecast period 2024-2031, growing from USD 42.05 billion in 2023 to USD 60.81 billion in 2031. The market worldwide has been progressing steadily with growing acceptance within agricultural industries for the need for balanced nutrient use to achieve the required yields and quality of crop production. Calcium, magnesium, and sulfur are significant secondary macronutrients that play many roles within plants, such as activating certain enzymes, chlorophyll synthesis, and movement of nutrients. They, however, are very important in restoring variations in soil nutrients, especially in soils that have undergone extensive agriculture and high cropping practices.
There are a number of reasons that encourage market growth, including a worldwide initiative for food security, a growing interest in better land management, and the need to improve crops’ ability to withstand the impacts of climate change. With the rise in demand for crops of higher value, which require sound management of nutrients, farmers are increasingly using secondary macronutrient fertilizers for specific crop purposes to achieve the set goals.
The market is becoming more efficient and environmentally friendly due to the introduction of advanced technologies in the manufacturing of fertilizers, such as slow-release and foliar application fertilizers. In the years to come, the global secondary macronutrient fertilizers market will continue to grow as farmers are under continuous pressure to increase crop productivity and quality with minimal economic and environmental costs.
In November 2023, EuroChem-BMU finished pilot tests for the manufacturing of mineral NPS fertilizers using elemental sulfur. The Russian market was decided to get the first 4-kiloton shipment of fertilizers containing sulfur. NPS compounds include elemental sulfur, one of the most important nutritional supplements needed for plant growth. For soils with low sulfur concentrations, the release of sulfur enhances the crop’s whole life cycle without requiring reapplication, increasing yields.
Technological Advancements to Catalyze Market Expansion
Advanced secondary macronutrient fertilizers are produced in such a way that they are more effective and friendly to the environment. Inventions like controlled-release technologies and methods of foliar application can aid in the delivery of the chemicals and minimize the loss of nutrients while optimizing plant absorption of the nutrients delivered.
The practice of applying fertilizers directly to the foliage in a technique known as foliar application helps to enhance the rate of absorption of nutrients by plants and is particularly useful in soils that are low in nutrients. These developments enhance the efficiency of fertilizers while minimizing their negative environmental impacts by reducing their leaching and runoffs.
Furthermore, companies are introducing new formulations to present better products to consumers. For instance, in February 2023, Vantage Ag, a maker and distributor of liquid fertilizer, introduced its first product using its in-house nanotechnology platform. The new technique uses a composition of nanoparticles that are very effective at covering and penetrating plant tissue. The sulfur particles in the new liquid sulfur product are less than a nanometer. Due to these microscopic particles, the nutrient is fully bioavailable and may be swiftly taken and used by the plant. Only 30 to 40 times the size of an atom, each nutrient particle is one-third to two-thirds of a nanometer.
Government Support to Influence Market Growth
Government involvement is one of the major factors estimated to propel the growth of the global secondary macronutrient fertilizers market. Balanced fertilization programs are motivated by governments and agricultural agencies globally, whereby secondary macronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur are promoted together with primary nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. The support includes grants, awards, and outreach, encouraging and teaching farmers about these nutrients to improve the soil and crops.
Culturally the farmers’ knowledge of sustainable management of nutrients. Also, the policies on food production intensive regions of soil degradation and nutrient loss are often associated with common government initiatives that supplement sustainability and food security advocate engaging in crop production of balanced and nutrient-dense fertilizers to circumvent loss in productivity of high-yielding crops.
Furthermore, some governments are easing the policies for manufacturers to enable them to produce these fertilizer products more efficiently. For instance, in July 2024, the European Council approved a rule requiring fertilizer items to be digitally labeled. While maintaining physical labels wherever needed, the legislation allows digital labels on fertilizing goods in the European Union. It makes labels easier to read and streamlines suppliers’ labeling requirements.
Calcium-based Fertilizers to Hold a Significant Market Share
Owing to its importance in plant growth and soil health, calcium occupies a significant portion of the market for secondary macronutrient fertilizers. Calcium serves as an important plant nutrient as it contributes to the fortification of the cell membranes of plants, which improves their ability to withstand damage by diseases and other external factors. In addition, calcium aids in the development of roots, thus enhancing the yield and quality of crops. Calcium plays a balancing role in soil by maintaining the pH range and preventing soil densification for ideal conditions for root development and moisture penetration. In mineral soils, calcium is present as the Ca2+ divalent cation, which can be absorb by plants. There is typically enough calcium available for the crop when the soil is limed to maintain an ideal pH level. By evaluating the cation on the soil’s CEC (cation exchange capacity), soil tests can calculate the amount of calcium that is accessible.
Calcium is a vital nutrient required in large quantities for crops such as tomatoes, apples, and lettuce that are economically significant. The awareness of the advantages offered by calcium has led to increased application of calcium-based fertilizers.
Asia-Pacific to Witness Rapid Market Growth
Asia-Pacific secondary macronutrient fertilizers market is showing tremendous growth, as the region boasts a large agricultural industry and an increasing demand for food security due to a growing population. Nations such as China and India, are putting secondary macronutrients fertilizers to promote crop production and mitigate the effects of degenerating soil caused by modern agricultural practices. The adoption is being further encouraged by government policies, encouraging balanced use of fertilizers and sustainable agriculture. However, the consumers’ inclination for quality, particularly for high value crops, is fueling the growth of the market.
To expand its activities in the region, especially in India, in March 2024, Haifa Group signed a collaborative agreement with Deepak Fertilizers and Petrochemicals Corporation Limited. With an emphasis on resource preservation and environmental pollution reduction, the new strategic partnership is aimed at giving Indian farmers access to cutting-edge plant nutrition solutions and efficient nutrigation techniques to increase crop yields and quality. In order to improve food security, increase farmer incomes, and boost India’s economy, the firms will collaborate to increase understanding of precision plant nutrition, with a focus on modern solutions that are accessible to Indian farmers.
Download Free Sample Report
Future Market Scenario (2024 – 2031F)
As farmers seek to achieve higher crop yields and greater quality, the growing awareness of the importance of secondary nutrients will boost demand.
Continued initiatives aimed at promoting agricultural sustainability will enhance the adoption of secondary macronutrients, especially in areas where soil nutrients are depleted.
The rising popularity of high-value, nutrient-dense crops will promote secondary macronutrient elements, especially in the production of horticulture and other unique crops.
Report Scope
“Secondary Macronutrient Fertilizers Market Assessment, Opportunities and Forecast, 2017-2031F”, is a comprehensive report by Markets and Data, providing in-depth analysis and qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current state of global secondary macronutrient fertilizers market, industry dynamics, and challenges. The report includes market size, segmental shares, growth trends, opportunities, and forecast between 2024 and 2031. Additionally, the report profiles the leading players in the industry, mentioning their respective market share, business models, competitive intelligence, etc.
Click here for full report- https://www.marketsandata.com/industry-reports/secondary-macronutrient-fertilizers-market
Latest reports-
Contact
Mr. Vivek Gupta 5741 Cleveland street, Suite 120, VA beach, VA, USA 23462 Tel: +1 (757) 343–3258 Email: [email protected] Website: https://www.marketsandata.com
#Secondary Macronutrient Fertilizers Market#Global Market Reports#Market Research Reports#Market Updates
0 notes
Text
Unlock the Benefits of Composted Pine Bark for Your Garden
Composted pine bark is increasingly recognized as a valuable addition to any garden. This natural material is an excellent soil amendment, offering multiple benefits that contribute to the overall health of your plants. By incorporating composted pine bark into your gardening routine, you can improve soil structure, enhance moisture retention, and reduce weed growth, making it an all-around beneficial choice for your outdoor space.
First and foremost, the use of composted pine bark helps to improve soil structure. Soils with poor structure can often lead to issues such as waterlogging or inadequate aeration, both of which are detrimental to plant health. However, when composted pine bark is added to the soil, it increases porosity, allowing for better air circulation and root penetration. This enhanced structure ensures that plants have access to the necessary nutrients and water, leading to more robust growth and healthier foliage.
Moreover, composted pine bark significantly boosts moisture retention in the soil. Many gardeners struggle with keeping their plants adequately hydrated, especially in regions with hot, dry climates. The spongy texture of composted pine bark helps to retain moisture, reducing the need for frequent watering. This not only conserves water but also ensures that plants have a consistent supply of moisture, which is crucial for their survival during dry spells.
In addition to improving soil structure and moisture retention, composted pine bark also plays a vital role in suppressing weeds. Weeds are a common problem in gardens, competing with desirable plants for nutrients, water, and sunlight. By applying a layer of composted pine bark mulch around your plants, you create a barrier that inhibits weed growth. This natural weed suppression reduces the need for chemical herbicides, making your garden more environmentally friendly.
Furthermore, composted pine bark is a sustainable choice for gardeners who are concerned about their environmental footprint. As a byproduct of the timber industry, pine bark that would otherwise be discarded is instead repurposed into a valuable gardening resource. By choosing composted pine bark, you are contributing to a more sustainable ecosystem, reducing waste, and promoting the use of natural materials in gardening practices.
Another significant advantage of using composted pine bark is its ability to slowly release nutrients into the soil. Over time, as the pine bark decomposes, it enriches the soil with essential nutrients that plants need for optimal growth. This slow-release process ensures a steady supply of nutrients, which is particularly beneficial for long-term plant health. Gardeners looking for a natural way to fertilize their plants will find composted pine bark to be an effective solution.
Additionally, composted pine bark enhances the aesthetic appeal of your garden. Its rich, dark color contrasts beautifully with green foliage, making your garden beds more visually appealing. Whether used as a mulch or mixed into the soil, composted pine bark adds texture and depth to your landscape design, creating a more polished and professional look.
To top it all off, composted pine bark is easy to use and widely available. You can find it at most garden centers or even create your own by composting pine bark at home. Its versatility makes it suitable for various gardening applications, from vegetable plots to ornamental flower beds. Whether you are a novice gardener or a seasoned expert, composted pine bark is a simple yet effective way to improve your garden’s overall health and appearance.
In summary, composted pine bark offers a range of benefits that make it an excellent choice for gardeners. From enhancing soil structure to reducing weed growth and promoting sustainability, this natural material is a must-have for anyone looking to create a thriving, eco-friendly garden. By incorporating composted pine bark into your gardening practices, you can enjoy healthier plants, a more beautiful landscape, and a garden that contributes positively to the environment.

0 notes